Researchers create digital twin to optimise DED repair process
January 13, 2023
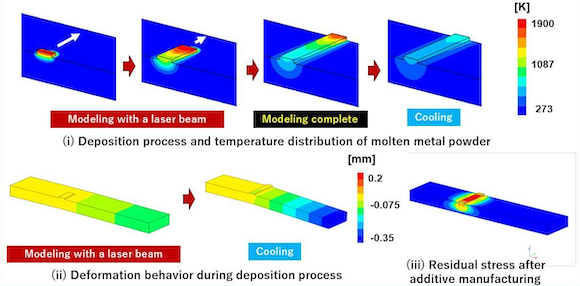
Researchers from Japan’s Tokyo University of Science (TUS) and Suwa University of Science, Nagano, have collaborated with Tocalo Co Ltd, Kobe, to publish a paper in Journal of Thermal Spray Technology outlining a numerical processing analysis system that automatically determines optimum forming conditions in Directed Energy Deposition (DED) Additive Manufacturing.
While DED helps overcome waste when repairing damaged parts compared to traditional Additive Manufacturing, the optimum forming conditions for DED are often a result of trial and error, the team explains. The developed numerical method is reported to automatically generate metal powder deposition elements and predict process forming conditions, temperature distribution, deformation state and residual stress distribution, in advance.
“The thermal radiation-thermal conduction model and the viscoplastic-thermoplastic constitutive model are applied to the stacked elements that constitute the deposited region, so that a wide range of state changes from melting to solidification of the deposited layer of metal powder can be faithfully simulated,” stated Professor Masayuki Arai, TUS. “By incorporating these models into a finite element analysis program, we have developed a new machining analysis system that has never been used before.”
The team numerically simulated the restoration process, and thus, predicted the forming process conditions, temperature distribution, deformation state, and residual stress distribution in advance and verified the findings through experiments. The research showed that the residual stresses in the deposited layer were much lower than those obtained via conventional repair processes.
This DED numerical analysis system is a digital twin of the existing core machining technology based on the fusion of metal in the area to be repaired. The numerical analysis method developed here could be further applied to various industrial applications, such as planning the repair of cavitation thinning on the surface of a blade used in power plant’s circulating pump and devising a method for reducing residual deformation after repairing the thinning of the tip of a gas turbine’s rotor blade.
Together, automation and the prediction of process conditions by the numerical machining analysis system is hoped to make by metal Additive Manufacturing repair by Directed Energy Deposition more effective and sustainable.
“Three-Dimensional Numerical Simulation of Repairing Process by Laser Direct Energy Deposition” is available here.
















