NIAR expands its metal Additive Manufacturing capability and adds industrial-scale X-ray CT system
July 17, 2017
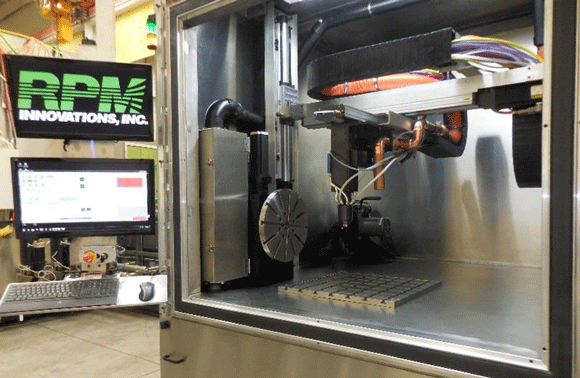
An RPMI 222 professional grade powder fed laser metal deposition system from RPM Innovations (RPM Innovations)
The National Institute for Aviation Research (NIAR), Wichita State University, USA, reports that it has expanded its metal Additive Manufacturing capability with the addition of a RPMI 222 professional grade powder fed laser metal deposition system from RPM Innovations.
The RPMI 222 Standard System has a 0.23 m3 build envelope and 2 KW fibre laser. The system incorporates a rotary table for cladding or building around a shaft. According to NIAR, the new RPMI 222 will be ready to take on client jobs by late July after routine installation, calibration and technician training.
“Additive Manufacturing has advanced dramatically in the last decade and permeated into just about every business sector,” commented Paul Jonas, NIAR’s Director of Special Programs. “The new RPMI system will enhance our capacity for prototyping, tool development and Additive Manufacturing research.”
NIAR performs industry-funded structural testing for Additive Manufacturing materials and parts and works directly with multiple standards organisations in the development of guidelines to standardise the materials, processes and quality of AM parts. The institute’s Additive Manufacturing Lab is home to multiple AM systems including a BAAM (Big Area Additive Manufacturing) system and additional capabilities ranging from the production of simple prototypes to high-strength, high-temperature parts using fused deposition modelling (FDM), polyjet, direct laser metal sintering (DLMS) and full-colour selective deposition lamination (SDL).
In addition to its acquisition of a new metal AM machine, the institute recently expanded its capabilities with the addition of several nondestructive inspection systems, including an industrial-scale digital X-ray and 3D computed tomography system, or X-ray CT.
The X-ray CT installed at NIAR is a multi-source (225/450 kV), multi-detector comprehensive system used to inspect small and large objects up to five feet without sectioning. This inspection system is used to visualise interior features of solid objects, improving processes such as failure analysis, quality control, troubleshooting manufacturing issues and the inspection of a variety of articles, including thick additively manufactured metallic structures.
Computed tomography is a high-fidelity NDI technique that reconstructs 3D images of an object, including its internal surfaces and interior details, from numerous micron-level 2D digital radiographic projections using smart computer algorithms and high-performance computing power. Digital radiographic images are generated by 360° rotation of the object on a motorised stage, placed in between a micro-focus X-ray source and detector.
NIAR’s acquisition of industrial scale nondestructive inspection systems was reportedly made possible through a Defense University Research Instrumentation Program of the USA’s Office of Naval Research (ONR). Waruna Seneviratne, technical Director of NIAR Composites Laboratory, was awarded $1.5 million for his proposal titled ‘X-Ray Computed Tomography for Nondestructively Inspecting Damage Initiation and Growth Mechanics of Composites and Bonded Joints under Fatigue Loading.’
















