Metal Additive Manufacturing for tool makers highlighted by AddUp and WBA
September 6, 2023
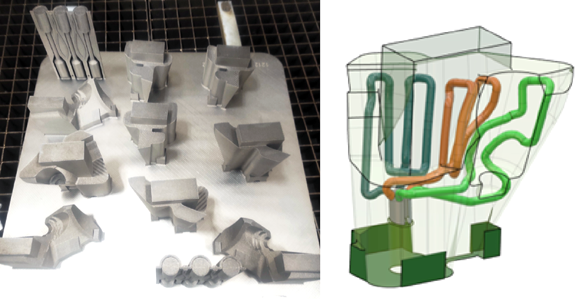
AddUp SAS, headquartered in Cébazat, France, has partnered with WBA Aachener Werkzeugbau Akademie (WBA), in Aachen, Germany, to demonstrate the advantages of metal Additive Manufacturing for the mould making industry. After launching a Tooling Study in January 2023, the team found six tool-making companies that each identified existing moulds to be tested. AddUp and WBA have now produced the first prototypes of these injection moulds, all with optimised internal cooling channels.
Traditionally, manufacturers using injection moulding must contend with certain constraints that are inherent to the moulding process. Specifically, the mould’s performance is directly related to its ability to cool the injected parts. However, AM technology can be used to create complex cooling channels that are positioned as close as possible to the mould walls. By adapting the shape of these channels to cool the surface of the part more homogeneously, manufacturers can improve the quality of their products and experience higher productivity, as well as reduced cooling and cycle times.
The companies selected for the Tooling Study were Pöppelmann, Siebenwurst, Harting, Zahoransky, GIRA, and Framas. They were given the opportunity to test the introduction of Additive Manufacturing into their workflow, and specifically implement the technical and economic advantages that AM technology brings to their injection moulds.
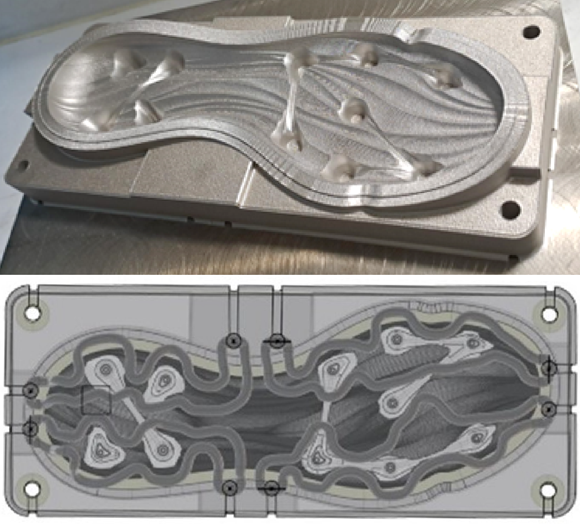

Once selected, AddUp and its partners evaluated each injection mould to determine how it could be optimised with Additive Manufacturing. Each part was then redesigned for AM, optimised for conformal cooling, and manufactured on AddUp’s 4-laser FormUp 350 Laser Beam Powder Bed Fusion (PBF-LB) Additive Manufacturing machine at AddUp’s AM Tooling Competence Centre in Aachen.
AddUp established its AM Tooling Competence Centre in Aachen, in partnership with WBA, in early 2023. This facility, which also serves as AddUp’s German subsidiary, gives tooling manufacturers access to AddUp’s Additive Manufacturing machines. Users can also submit application cases for evaluation and study of all aspects of their project, from the design when applied to PBF-LB, to profitability analysis and study of series production.
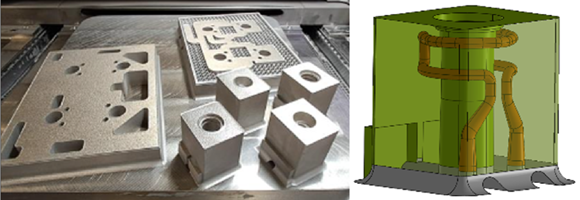

AddUp explained that the choice of material is critical for tool makers, as moulds must meet high requirements, especially in terms of corrosion resistance, heat conductivity, and fatigue. Leveraging its twenty years of experience in AM, AddUp used Maraging 300, a material successfully used in series production by Michelin to manufacture over a million tyre mould sipes per year. In addition to Maraging 300, AddUp recently announced build parameters for AISI 420, a corrosion-resistant tool steel also known as 1.2083 in the German standard. It is expected that this new material will enable tooling manufacturers produce even more complex and efficient moulds.
For the project, post-processing was completed by the tooling company itself or by the WBA. Each of these ready-to-use moulds is now being sampled on the respective tooling company’s production lines, and the comparative data will be provided to WBA. The final results of the Tooling Study will be presented and published at the WBA’s General Assembly in late 2023.
This study was also supported by companies including iQTemp, Deutsche Edelstahlwerke, 3D Laser BW, and Siemens NX, as well as institutes, such as Fraunhofer ILT and ACAM.
AddUp plans to launch a follow-up Tooling Study this autumn, and is inviting any tool makers interested to get in touch.
Download Metal AM magazine

















