Properties and standards for metal Additively Manufactured parts
Properties of metal AM parts
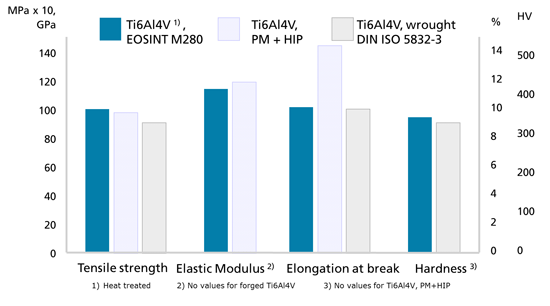
As the way materials are processed in metal AM differs from the processing method of other metal manufacturing technologies, it follows that the microstructure, defects, and therefore properties of metal 3D printed parts will differ as well. As a general rule, most metal AM parts will meet or exceed the property requirements of cast parts. Wrought properties are by far the most challenging to equal; however, heat treatment or HIP processes applied post-build are often successful in equalling wrought properties.
It is somewhat unfortunate that, for metal Additive Manufacturing processes to be accepted, parts must abide by the property requirements set by conventional processes. Like the use of conventional alloys, it makes much more sense for a new set of property specifications to be developed for AM processes. However, to gain more widespread acceptance, AM processes must currently fit within the conventional materials and processing certification frameworks.
Standards for metal AM parts
The international body governing all worldwide standards is the International Standards Organization (ISO). Various countries and jurisdictions around the world have their own standards bodies, but work is coordinated by ISO so that standards can be globally harmonised. For an industry as globally relevant as AM, internationally harmonised standards are the only way to standardise and therefore further develop and rapidly commercialise metal 3D printing technologies.
Standards for metal Additive Manufacturing cover all aspects of the technology, from the definition of AM process terminology, to defining test conditions, the specification of feedstock materials, supplier agreements, property requirements, and build conditions. In addition to these AM-specific standards, many industry-specific standards also apply to metal 3D printed parts, such as aerospace and medical standards.
Initially, the ISO/TC261 committee set out several standards specific to AM. However, the ASTM (the American Society for Testing and Materials) F42 committee has developed many more standards pertaining to AM via its Centers of Excellence, member countries, and small grants scheme. As a result, ISO and ASTM have more recently been jointly developing many standards for AM. Participating countries around the world can be involved in standards development via their own standards bodies. Participation is via joint working groups.
> Next page: Applications for metal Additive Manufacturing technology
Download Metal AM magazine