Farsoon’s SRS technology reduces need for supports in metal Additive Manufacturing
April 23, 2024
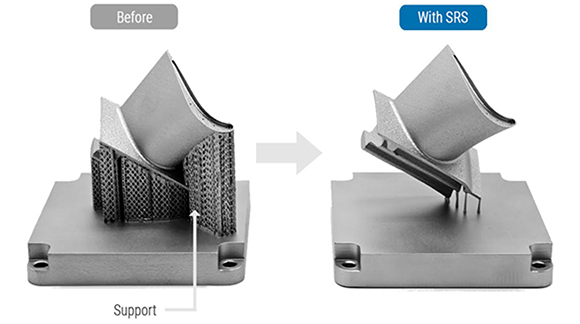
Farsoon Technologies, based in Changsha, China, first introduced its Support Reduction System (SRS) technology at TCT Asia 2023. The company has now released further information on the novel process, which it says requires significantly fewer supports when compared to standard metal Laser Beam Powder Bed Fusion (PBF-LB) Additive Manufacturing.
The development of the company’s SRS technology is said to address the internal stress and deformation during the cooling phase of metal PBF-LB, which can lead to part failure, especially in overhanging structures.
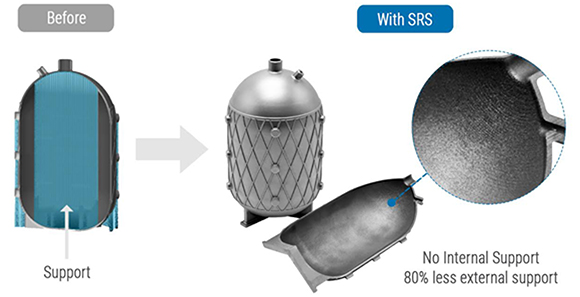
A core feature of this is the ability to fabricate inverted conical structures and horizontal circular holes with no support. Applicable to all Farsoon metal PBF-LB platforms, the new SRS technology can successfully form inverted conical structures with a 20-25° angle and support-free horizontal circular holes up to 50 mm in diameter.
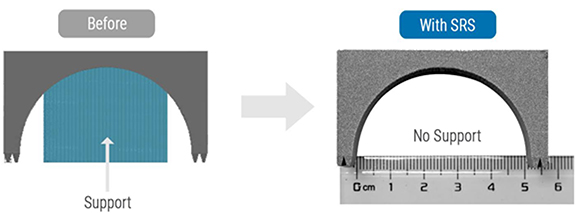
The advancement significantly reduces the need for support structures traditionally necessary for low-hanging angles (typically below 45°) to mitigate the risk of part failure. This not only saves on material costs and reduces manufacturing and post-processing time but also minimises potential damage to the part, enhancing both efficiency and quality in sectors like aerospace and automotive.
The use of Farsoon’s slicing software and scanning strategies allows for precise control of energy input and local part temperature. This ensures high part density and significantly improves the capability of forming low-angle structures over traditional scanning technologies.
The SRS support-reduction technology reportedly offers increased design freedom and reduces the constraints imposed by traditional manufacturing methods. For example, a closed impeller made of IN718 material, approximately 130 mm in diameter and 50 mm in height, can now be manufactured 33% faster, with cost reductions exceeding 25%.
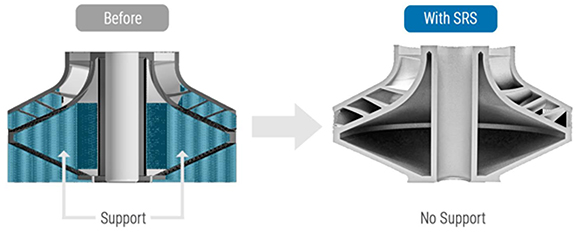
Farsoon has applied this minimal-support technology to a variety of real-world materials and applications, including titanium, high-temperature, and aluminium alloys and stainless steel. Applications range from combustion chambers to closed impellers, valve bodies, and nozzles, with the largest parts exceeding 450 mm.
Download Metal AM magazine

















