Researchers use MEX-based AM for graded porosity in titanium components
November 23, 2022
Tailoring the surface area and the porous structure of metal parts is of interest to a variety of markets, including the health sector. By introducing porosity into orthopaedic implants, manufacturers can control the part stiffness and improve its biological fixation via reconstructive cellular activity. Titanium alloys in particular are widely used for their biocompatibility, high specific resistance and corrosion behaviour, but have been called too rigid compared to bone, which can lead to bone loss surrounding the implant.
To counter this negative effect, researchers from the University of Lyon have published research in Advanced Engineering Materials which details the use of metallic inks (Ti6Al4V powder mixed with hydrogel) to additively manufacture cellular scaffolds with a tuneable pore architecture in terms of size, fraction and interconnectivity.
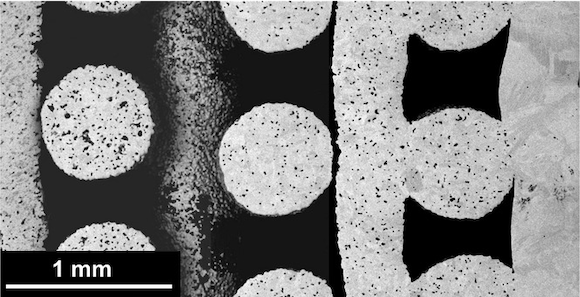
After Additive Manufacturing by Material Extrusion (MEX) process direct ink writing (DIW), followed by debinding and sintering, the fraction and size of macropores (μD>100 μm, designed by CAD) and micropores (μD<10 μm, remaining after sintering), the roughness and the microstructure of the parts were determined by high-resolution X-ray tomography and electron microscopy.
“Sinter-Based Additive Manufacturing of Graded Porous Titanium Scaffolds by Multi-Inks 3D Extrusion” reports that adjusting initial powder size correlated with different pore architectures, from interconnected micropores to fully dense filaments. This discovery was combined with the multi-inks DIW approach to fabricate structures with graded microporosity.
This new ability may prove promising for the production of functional materials, such as biomedical scaffolds or implants, with tuneable osseointegration, stiffness, and strength. The micropores could also be loaded with active molecules and positioned according to release needs.
The paper is available to read here, in full.
















