Chinese scientists develop liquid phase 3-D printing method using low melting metal alloy ink
October 5, 2014
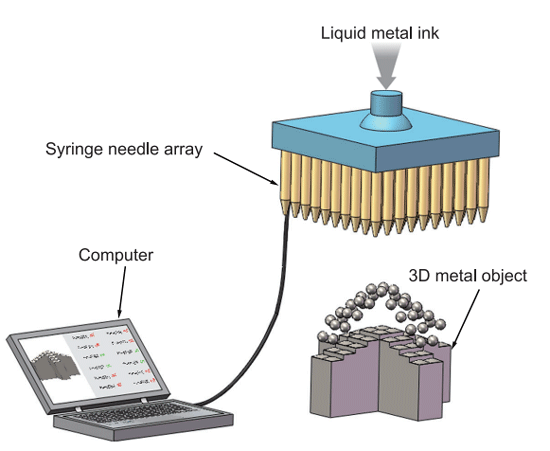
Scientists at the Beijing Key Laboratory of Cryo Biomedical Engineering, part of the Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry at the Chinese Academy of Sciences, have developed a new conceptual 3D printing method with “ink” consisting of a metal alloy that has a melting point slightly above room temperature.
Conventional 3D metal printing is generally restricted to metals with a high melting point, and the process is rather time consuming. In a new study published by the journal SCIENCE CHINA Technological Sciences, researchers Liu Jing and Wang Lei present a liquid-phase 3D printing technique for the rapid manufacturing of a conductive metal object in one, two or three dimensions. Compared with air cooling in conventional 3D printing, their liquid-phase manufacturing process prevents the metal ink from oxidation.
The scientists state that metals with a low melting point, especially metals that melt at room temperature, have attracted attention in the areas of computer chip cooling, thermal interface materials, and microfluidics. “Such material has also been proposed as printing ink with evident value in direct writing electronics and 3D printing technology,” added the researchers. In their new study, a four-element alloy, Bi35In48.6Sn16Zn0.4, was developed and adopted as the printing ink.
The printing ink is dropped into a liquid phase cooling fluid via an injection needle and the object is printed layer by layer. During the process of liquid phase 3D printing, several factors affect the final printing quality. The types and properties of the printing ink dominate the fabrication process. In principle, any metal with a low melting point (or less than 300°C) can be selected as a printing ink on condition that an appropriate cooling liquid is available. The ink material can be an alloy based on gallium, bismuth, or indium, or even a mixture of these alloys and nanoparticles.
The authors state that compared to conventional metal prototyping techniques, liquid phase 3D printing offers several distinct advantages. It offers a relatively high speed of manufacturing and allows for 3D electromechanical systems to be printed. For example, a conductive liquid metal can be used in conjunction with nonmetal materials (such as plastic) to form 3D functional devices that include supporting structures and conductive devices.
![]() Join the Metal Additive Manufacturing group
Join the Metal Additive Manufacturing group
Subscribe to our FREE e-newsletter
Useful links: News | Articles | Introduction to metal Additive Manufacturing