Castor releases update to identify Additive Manufacturing possibility from 2D drawings
July 22, 2022
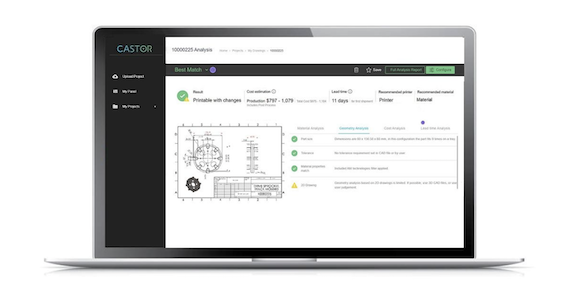
Castor Technologies Ltd, Tel Aviv, Israel, has released an update to its parts identification software which enables it to automatically analyse 2D drawings and provide recommendations on what parts of the drawing are well suited to Additive Manufacturing. This is intended to make Additive Manufacturing technology more accessible to companies whose manufacturing is based primarily on 2D drawings, some of which may be decades old, rather than CAD files.
The technology behind Castor’s 2D analysis is based on computer vision that interprets the geometry & product manufacturing information (PMI) of each part and machine learning models that have gained insights over due to the regular upload of parts to Castor.
“Castor is expanding its value proposition by offering many companies, which were not able to assess the compatibility of 3D printing to their organisation until now, a feasible way to automatically analyse their design files and gain deep valuable data and knowledge regarding the potential of AM for them,” stated Omer Blaier, co-founder & CEO of Castor. “We give these organisations a tool that helps them find new business cases and discover opportunities to reach their initiatives and 3D printing goals, using their existing 2D design files”.
Castor’s software enables users to upload thousands of parts from 2D drawings simultaneously. Once parts are uploaded, the software automatically extracts PMI (product manufacturing information) out of PDF files of 2D Drawings and calculates parts’ size, volume, complexity etc., based on dimensions from projected views. The software then suggests additive manufacturability of parts, recommends optimal technology & materials, and performs a financial analysis of Additive Manufacturing compared to traditional manufacturing. It then exports this information as a formal PDF report and a raw data excel sheet.
Once the selected files are in a 3D format, the software can also deliver recommendations for re-designing parts for Additive Manufacturing (DfAM) – such as part consolidation and weight reduction. The capabilities enable quick assessment of a part’s likeliness to fail using a Finite Elements Analysis.
















