German researchers showcase electric motor produced entirely by Additive Manufacturing
May 7, 2018
Video showing the extrusion-based Additive Manufacturing process used to produce the motor (Courtesy TU Chemnitz)
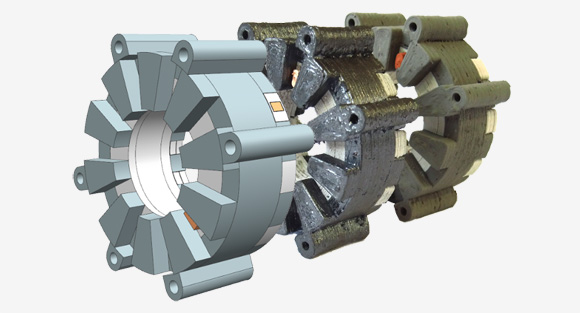
During Hannover Messe 2018, researchers from Chemnitz University of Technology (TU Chemnitz) in Germany showcased what is thought to be the world’s first electric motor produced entirely by Additive Manufacturing. The motor was produced using a method in which highly viscous metallic and ceramic pastes were extruded through a nozzle to build the body of the part in layers, before sintering to the required hardness, in a process the team refers to as ‘Multimedia 3D Printing’.
Development of the motor was led by Dr Ralf Werner, head of TU Chemnitz’s Professorship of Electrical Energy Conversion Systems, and two members of the professorship’s academic staff, Johannes Rudolph and Fabian Lorenz, who in 2017 presented an additively manufactured coil produced using the same extrusion technique and said to be capable of withstanding temperatures over 300°C.
Since that time, the team reported that it has successfully printed all of the key components of its electric motor, including copper electrical conductors, which create magnetic fields in combination with iron or iron alloys, and ceramic electrical insulation, which insulates the conductors from each other and from the iron components, referred to as the magnetic circuit.
A stator for a winding-less reluctance machine produced by the researchers. Left: CAD model, middle: sintered stator, right: green part before heat treatment (Courtesy Johannes Rudolph)
“Our goal over the last two and a half years was to dramatically increase the temperature that electrical machines are capable of withstanding,” explained Dr Werner. The researchers achieved this by replacing conventional polymer-based insulation materials with specialised ceramics, which have a much higher temperature resistance. “The maximum permissible winding temperature of 220°C associated with conventional insulation systems can then be exceeded by a significant amount,” added Rudolph.
As well as having greater temperature resistance, the ceramic insulation material is said to possess a higher degree of thermal conductivity, enabling heat generated by the conductors to be more easily dissipated and increasing the output density of the motor.
The researchers stated that they intend to develop the ‘Multimedia 3D Printing’ method used to produce the motor for introduction into the market, with Rudolph and Lorenz preparing to launch a spin-off company based around the technology. “The motor that was printed in the Chemnitz University Laboratory represents a breakthrough and is at the same time the proof of principle – that is, it demonstrates the feasibility of our technology,” Rudolph stated.
















