UNIST researchers develop thermoelectric technology to produce power-generating tubes using AM
September 3, 2021
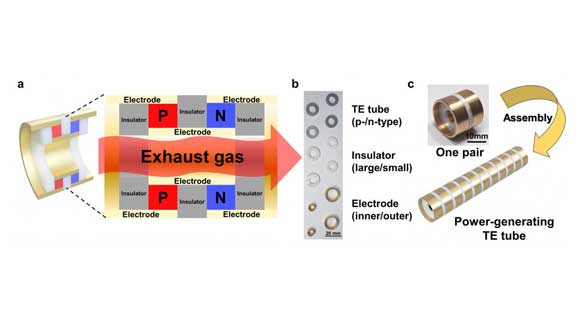
A research team, affiliated with Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST) located in Ulsan, South Korea, have successfully developed a thermoelectric technology to produce power-generating tubes using Additive Manufacturing.
In this study, researchers created the thermoelectric tube using an additively manufactured ink made of lead (Pb) and tellurium (Te). Metal particles were mixed inside a glycerol solvent to provide viscoelasticity, a status that exhibits both viscous and elastic characteristics. The tube has a high thermoelectric performance at temperatures between 400 and 800°C, which is the temperature range of a car’s exhaust gases. The tube shape reportedly makes it more effective in collecting heat than a conventional cuboid type.
The research study was jointly led by Professor Han Gi Chae and Professor Jae Sung Son from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, and Professor Sung Youb Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering at UNIST. The following researchers jointly participated in the study: Professor Sangjoon Ahn, Dr Jaehyung Hong, Professor Ji Eun Lee from Chonnam National University, and Jeongin Jang from Korea Electrotechnology Research Institute.
“Through this research, we will be able to effectively convert heat generated by factory chimneys, the most common type of waste heat source, into electricity,” stated Professor Son. He explained this is because the existing thermoelectric devices were in rectangular parallelepiped shapes.
Professor Chae added, “If we use 3D printing technology in the production of thermoelectric materials, we will be able to overcome limits of conventional materials. The new technology for providing viscoelastic characteristics to 3D printed materials will be used in various other sectors.”
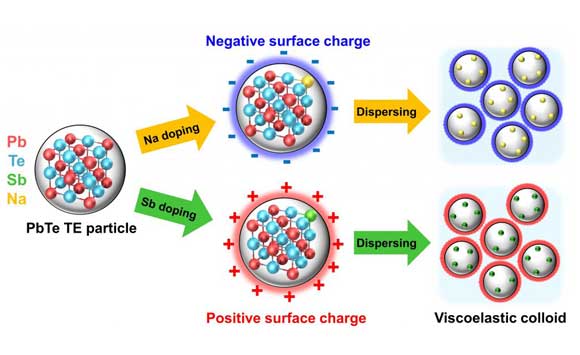
The findings of this research were published in Advanced Energy Materials on April 15, 2021, under the journal reference: Jungsoo Lee, Seungjun Choo, Hyejin Ju, et al., “Doping-Induced Viscoelasticity in PbTe Thermoelectric Inks for 3D Printing of Power-Generating Tubes,” Adv. Energy Mater., (2021).
















