Clinical trial of Renishaw’s Parkinson’s drug delivery device nears completion
February 27, 2020
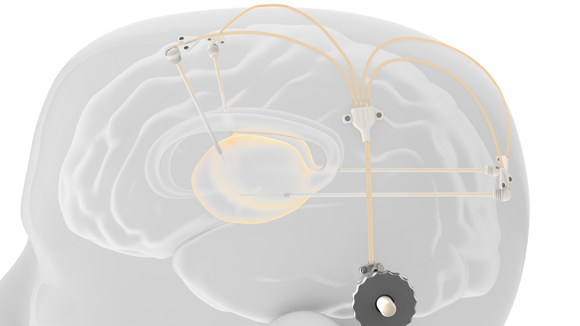
Renishaw plc, Wotton-under-Edge, Gloucester, UK, has announced the completion of the main part of a multi-centre clinical trial, jointly undertaken with Herantis Pharma plc, for the treatment of Parkinson’s Disease through the use of a metal additively manufactured intraparenchymal drug delivery device to transport cerebral dopamine neurotrophic factor (CDNF) directly into the brain.
Parkinson’s is a neurodegenerative disease caused by the breakdown of dopamine-producing neurons in the brain. Symptoms include involuntary shaking, stiffness of muscles and a slowing down of movement, which can be extremely debilitating. In addition, patients can suffer associated non-motor symptoms such as difficulty sleeping, memory loss, anxiety and depression.
Whilst these symptoms can initially be managed with medication, there is currently no treatment available that effectively prevents disease progression, or that treats the motor and non-motor symptoms together.
Renishaw and Herantis Pharma’s clinical study’s repeated delivery regime, which allows for a prolonged therapeutic window, is thought to be crucial to achieve the potential neuroprotective and neurorestorative actions of CDNF, and was made possible through the use of Renishaw’s new drug delivery system.
Initial results of the Phase 1-2 study indicate predictable and accurate placement of the device as well as its positive performance and safety. The company will continue to assess the results as the data is analysed and through the extension part of the study, as patients receive ongoing monthly infusions of CDNF using the device.
Rupert Jones, Managing Director of Renishaw Medical, stated, “The results of this trial and the performance of Renishaw’s drug delivery system are promising for the many people with Parkinson’s disease and I would like to take this opportunity to thank the trial participants for making this possible.”
“These results allow us to build towards CE marking of Renishaw’s device so that further neurodegenerative and neuro-oncological conditions can benefit from our technology,” he continued. “We see our device as an enabling technology that facilitates the reliable and repeated delivery of therapeutic agents direct to targets deep within the parenchyma, as part of a paradigm shift in the way treatments of neurological disorders and brain tumours are progressing.”
Renishaw’s intermittent drug delivery system comprises up to four catheters, which can be implanted into target areas within the brain. The catheters are accessed via an additively manufactured titanium transcutaneous port implanted behind the patient’s ear.
Drug-filled infusion lines are then connected using an MRI compatible application set, which repeatably locates onto the port. Retractable needles extend through a septum in the port to enable therapeutics in the external infusion lines to be infused through the implanted catheters.
Using this patented design, patients are able to receive infusions in an outpatient setting, rather than requiring the reimplantation of new catheters for each infusion, which has been the only option for many trials to date.
This study was a first-in-human study whereby seventeen patients were randomised to receive either one dose per month for six months of a placebo, or six increasing doses of Herantis Pharma plc’s novel drug candidate, CDNF, over the same period in a blinded manner. After this six month period, patients may now enter into an additional six-month study where all participants receive CDNF. In total, patients will receive twelve infusions, all delivered in an outpatient setting.
The primary endpoints evaluate the safety, performance/tolerability of both the drug delivery system and CDNF, as well as the surgical accuracy. Secondary to this, the potential efficacy of the drug, rated against the Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS) motor score evaluation, was also monitored.
The clinical study has received funding from the European Union’s research and innovation programme Horizon 2020 under the grant agreement number 732386.
















