Advanced Innovative Engineering uses Additive Manufacturing to re-engineer rotary engines
May 25, 2021

Advanced Innovative Engineering (AIE), a manufacturer of rotary engines based in Lichfield, Staffordshire, UK, has turned to Additive Manufacturing to improve the performance of its engines. The goal for the company, located at the heart of the UK’s aerospace engineering and manufacturing industries, was to investigate the suitability of AM to reduce weight, cut product development and manufacturing lead times and lower production costs.
Through the DRAMA (Digital Reconfigurable AM facilities for Aerospace) project, led by the UK’s Manufacturing Technology Centre (MTC), engineers from the National Centre of Additive Manufacturing (NCAM) based at the MTC visited AIE to gain an understanding of the products currently manufactured and the processes involved. NCAM then split the project into three distinct activities:
- AIE rotary housing – conceptual fin designs: Fin designs were to be constrained, thereby maximising heat dissipation within the motor housing, whilst remaining within the original engine geometry bounds and minimising weight. A variety of fin geometries fell into approximate categories: honeycomb lattice, TPMS Gyroid lattice and algorithmic tree. Each were developed within the constraints allowed before being additively manufactured. This allowed AIE to assess as-built surface roughness and the potential for manufacturing and functionality issues.
- Thermal/structural FEA simulation: The two preferred fin designs and primary engine components (engine housing and front & rear end plates) underwent structural simulations to assess areas of critical concern for stress values below yield point criteria for aluminium under the scenarios modelled.
- AM process selection: Laser Beam Powder Bed Fusion (PBF-LB) was selected as the most appropriate AM process. A build layout was created and demonstrator parts were additively manufactured using a Renishaw 500Q AM machine.
NCAM engineers, with this testing criteria, have succeeded in helping AIE to reduce the engine mass from 6 kg to 4 kg, reduce component count significantly and, therefore, manufacturing costs, while maintaining the engine’s operational capability.
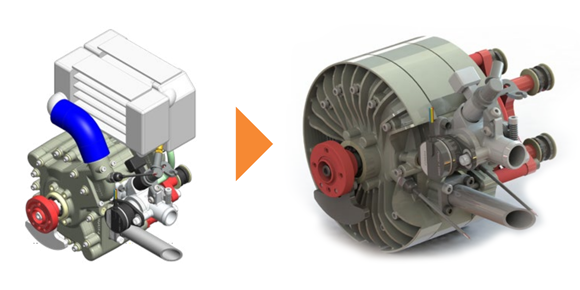
Encouraged by these results, AIE expects to pursue this with a follow-on project to further explore the thermal sensitivity of the assumed input parameters, as well as considering convective and radiative heat transfer interactions between surface. Further CFD studies of the fluid flow over the engine will also be undertaken to more accurately assess flow characteristics through the fin designs and better inform design for a full production version.
“Accessing the expertise of NCAM through the DRAMA programme has been instrumental in enabling AIE to develop an understanding of metal Additive Manufacturing, its potential applicability to its engine designs and the solutions it can provide over and above traditional manufacturing processes. DRAMA really has been a game-changer for AIE, reshaping our approach to product design through seeing what is possible using AM,” stated Nathan Bailey, Managing Director, AIE.
DRAMA project partners include MTC, ATS, Autodesk, Granta Design, MAA, NPL, Renishaw and the University of Birmingham.
















