Additive Manufacturing of highly-stressed components in hardened martensitic stainless steel
February 22, 2021
The Institute of Production Engineering and Machine Tools (IFW), part of the Hannover University’s engineering centre (PZH) in Garbsen, Germany, and the Fraunhofer Institute for Additive Manufacturing Technologies (IAPT), part of the Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft research organisation, Hamburg, have collaborated on a new Additive Manufacturing research project, AddSpin.
For AddSpin, the two institutes investigated to what extent Laser Beam Powder Bed Fusion (PBF-LB) Additive Manufacturing is suitable for tightly-toleranced, highly-stressed machine components, with the goal of reducing machining and non-productive times of machine tools by reducing mass and, thus, the moment of inertia.
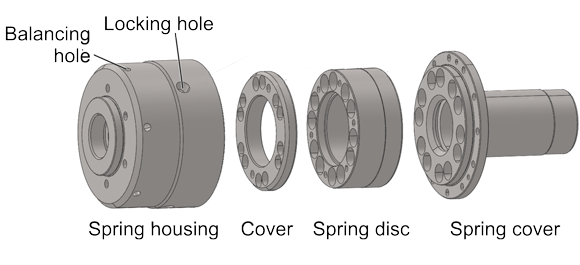
The potential was demonstrated using the clamping system of the sliding headstock automatic lathe from INDEX-Werke GMBH & CO KG Hahn & Tessky, Esslingen. For this purpose, four components of the installed clamping system – spring housing (AlZn5,5MgCu), the movable components spring disk (16MnCr5), cover and spring cover (both CF53) – from Hydronic-hiestand Hydraulik & Elektronik GmbH, Pfullendorf, were selected, which offer high potential for the reduction of the moment of inertia.
One aim of the project was the selection and qualification of a material that is suitable for both the application and the AM process: X5CrNiCuNb16-4, a precipitation-hardened martensitic stainless steel, was chosen for this study.
At the beginning of this qualification process, suitable parameters were determined. Based on parameters of already-known steel materials, test specimens were produced by varying the process speed, laser power and layer thickness; these were then analysed for their density. The combination of parameters which allowed both high density and build-up rate was selected for the production of further test parts and components.
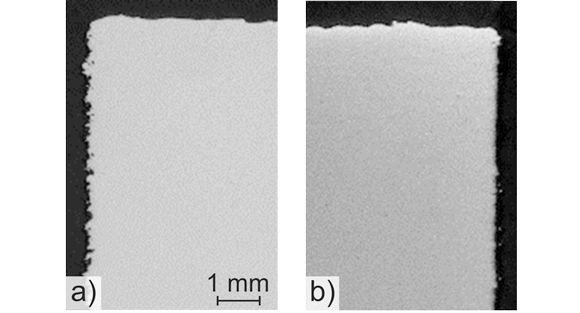
In the next step, the surfaces of the components were optimised by adjusting the process parameters for the component contour, reducing the roughness of the lateral surfaces to below 6 µm.
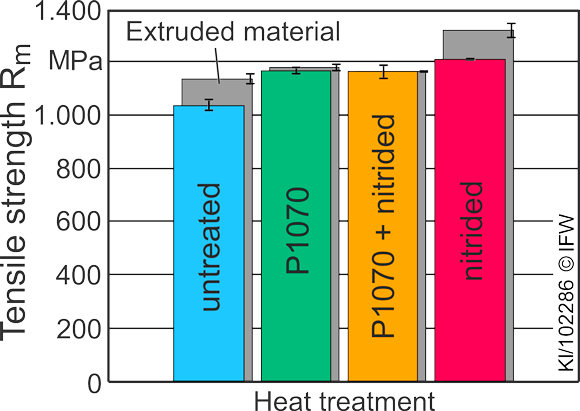
The mechanical properties were then characterised under different heat treatment conditions. In addition, extruded reference samples were produced. For all eight sample types, the moduli of elasticity, tensile strength, yield strength, hardness and wear rates were determined experimentally. The samples showed tensile strengths of more than 1000 MPa without heat treatment, with possible tensile strengths of up to 1200 MPa achieved through targeted post-treatment.
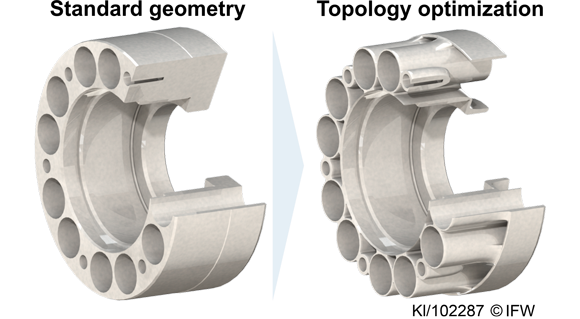
Using the determined values, a topological optimisation was subsequently performed using ANSYS simulation software. A minimisation of the mass was determined and it was shown that the component masses can be reduced by up to 67%.
In relation to the entire rotary system, the optimisation of these four components already results in a 19% reduction of the moment of inertia. For the process step of taper turning at constant cutting speed, for example, results show a theoretical reduction of 19% in machining time.
The verification of the theoretical productivity increase will be conducted in future by practical tests under real operating conditions. For this purpose, the AM components will be installed in the automatic lathe and machining tests will be carried out. The knowledge gained will be summarised in the form of a final guideline for the production-oriented design of highly stressed components.
The IGF project 20276 N of the Research Association VDW Werkzeugmaschinen e.V. was funded via the AiF as part of the program for the promotion of joint industrial research (IGF) by the Federal Ministry of Economics and Energy based on a resolution of the German Bundestag.
www.ifw.uni-hannover.de/en/institute
www.iapt.fraunhofer.de/en.html
Authors:
Heinrich Klemme, Institute of Production Engineering and Machine Tools (IFW), Leibniz University Hannover, Germany
Heiko Blunk, Fraunhofer Institute for Additive Manufacturing Technologies (IAPT), Hamburg, Germany
















